Conflict minerals – tantalum, tin, tungsten, and gold – are increasingly linked to human rights abuses and environmental degradation in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and other regions. The extraction of these minerals, often through forced labor and violence, has become a significant concern for international organizations, governments, and consumers. Understanding the complexities of this issue and implementing effective solutions is crucial for promoting responsible supply chains and ensuring ethical sourcing. This article provides a comprehensive guide to creating and utilizing a Conflict Minerals Reporting Template, equipping businesses and stakeholders with the tools to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with conflict minerals. The core of this guide revolves around the importance of transparency and accountability in the mining sector. Conflict Minerals Reporting Template – a standardized framework for documenting and reporting on the origin and impact of conflict minerals. It’s not just about compliance; it’s about fostering trust and driving positive change. This template aims to streamline the process, improve data collection, and ultimately contribute to a more sustainable and ethical mining industry.
The rise of conflict minerals has dramatically increased public awareness and scrutiny. Consumers are increasingly demanding to know where their products come from, and businesses are facing growing pressure to demonstrate their commitment to ethical sourcing. The recent focus on the DRC, particularly the allegations of child labor and forced labor within artisanal mines, has highlighted the need for robust monitoring and verification systems. The lack of consistent and reliable data has hampered efforts to effectively address these issues. That’s why the development of a standardized reporting template is so vital. It provides a common language and framework for all stakeholders – miners, suppliers, buyers, and consumers – to communicate concerns and collaborate on solutions. Without a clear and accessible tool, the problem remains largely unaddressed, perpetuating a cycle of exploitation and environmental harm. The very existence of the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template is a testament to this growing demand for responsible practices.
The term “conflict minerals” encompasses a range of minerals – tantalum, tin, tungsten, and gold – that are often linked to human rights abuses and environmental destruction in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and other regions, particularly in the eastern part of the country. These minerals are mined through a complex and often brutal system, frequently involving forced labor, child labor, and violence. The DRC is the primary source of conflict minerals, but other countries, including Myanmar, the Philippines, and Indonesia, also face significant challenges related to the extraction of these resources. It’s important to note that the link between conflict minerals and human rights abuses is not always straightforward. While some mines may be associated with violence, others may be operating under exploitative conditions. Furthermore, the complexity of the supply chain – involving numerous intermediaries and subcontractors – makes it difficult to trace the origin of minerals back to specific sources. This is where the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template comes into play.
The impact of conflict minerals extends far beyond the immediate mining communities. The extraction of these minerals often leads to deforestation, soil degradation, and water pollution. The use of child labor and forced labor further exacerbates these problems, depriving children of education and subjecting them to dangerous working conditions. The environmental consequences are significant, contributing to biodiversity loss and climate change. The Conflict Minerals Reporting Template helps to mitigate these negative impacts by providing a mechanism for tracking and reporting on the entire supply chain. It allows businesses to identify and address risks at each stage, from raw material sourcing to final product distribution. This proactive approach is essential for creating a more sustainable and ethical mining industry.
![]()
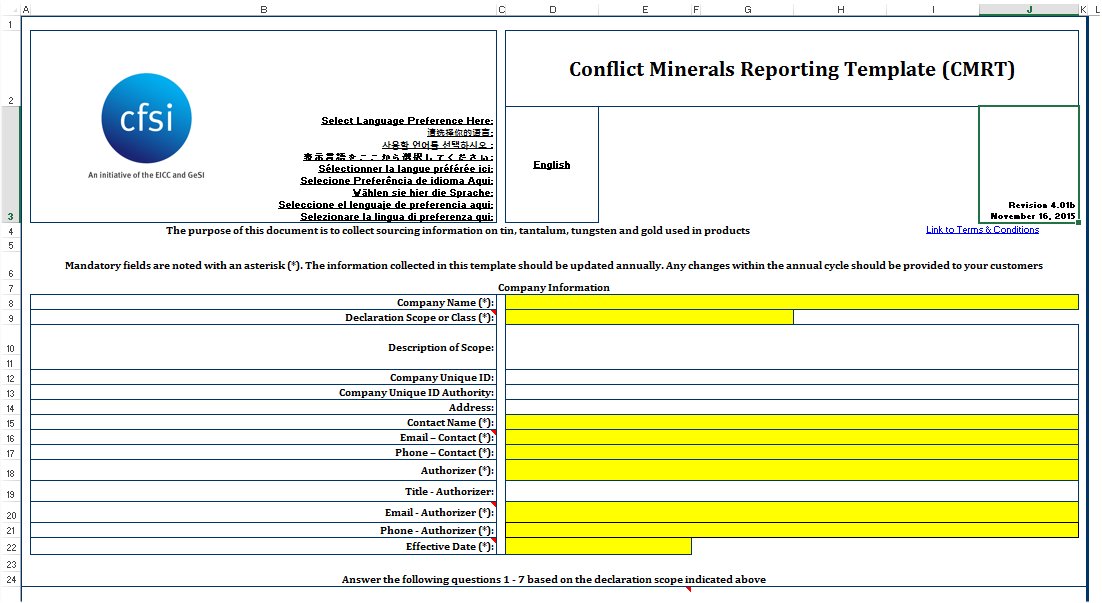
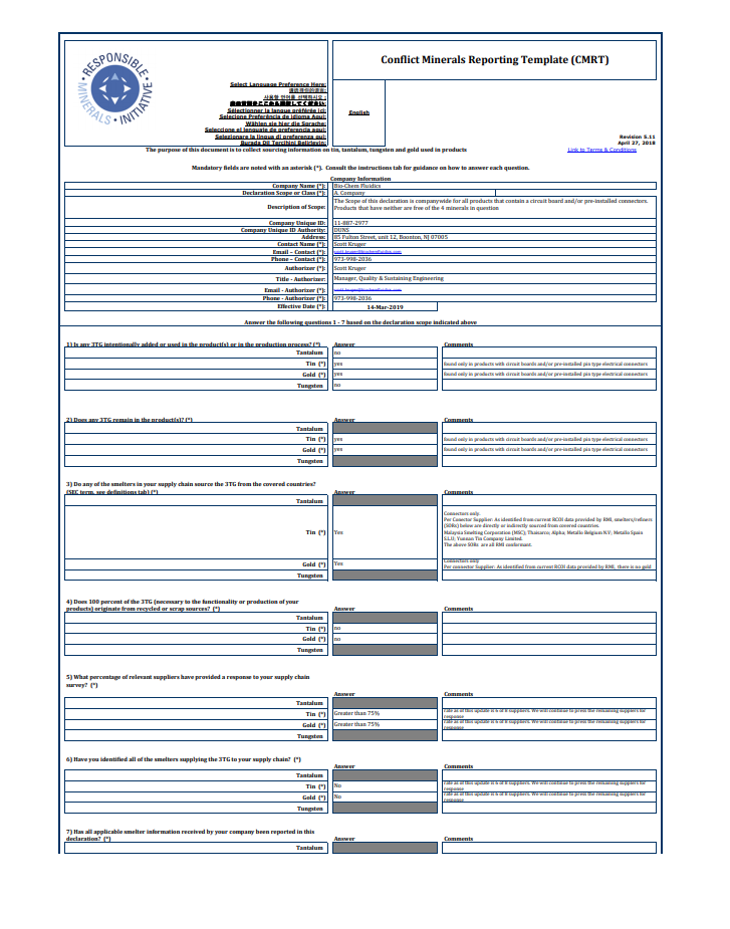
The Conflict Minerals Reporting Template is structured to facilitate comprehensive data collection and analysis. It’s divided into several key sections, each addressing a specific aspect of the supply chain. The template encourages detailed documentation of sourcing practices, including information on:

Mineral Source: This section requires the precise location of the mine or operation where the mineral is extracted. It should include the name of the mine, the country, and the specific region.
Supplier Information: This section details the supplier’s name, address, and contact information. It’s crucial to verify the supplier’s compliance with ethical sourcing standards.
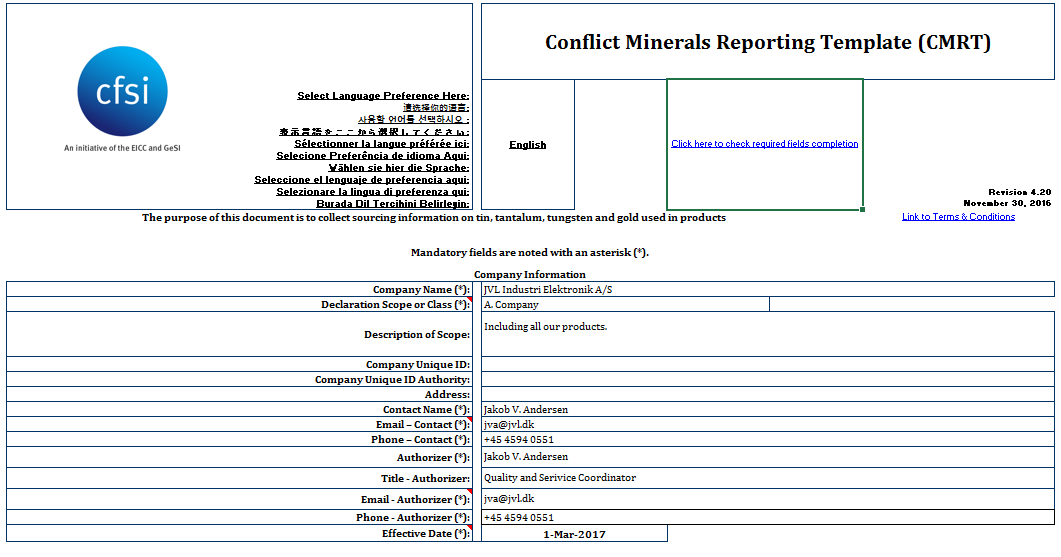
Traceability Data: This is the core of the template, requiring detailed information on the origin of the mineral. This includes information on the chain of custody, the processing methods used, and the labor practices employed. Specific fields will address the type of processing (e.g., refining, smelting) and the labor conditions.

Labor Practices: This section addresses labor standards, including the presence of child labor, forced labor, and unsafe working conditions. It requires documentation of training programs, health and safety protocols, and grievance mechanisms.
Environmental Impact: This section assesses the environmental impact of the mining operation, including water usage, waste disposal, and deforestation. It should include data on pollution levels and mitigation measures.

Community Engagement: This section documents the engagement with local communities, including consultations, compensation programs, and support for local development initiatives.

Certifications & Standards: This section lists any relevant certifications or standards that the supplier has adopted, such as the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) or the Trace Noble Group.
Data Collection Methods: This section outlines the methods used to collect data, including surveys, interviews, and audits. It’s important to ensure that data collection is conducted ethically and with respect for human rights.
The effectiveness of the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template hinges on the integrity and accuracy of the data collected. This requires robust verification processes, including independent audits and third-party assessments. Businesses must invest in training their staff on data collection and reporting procedures, and they must establish clear protocols for addressing any discrepancies or inconsistencies. Furthermore, transparency is paramount. All data collected should be publicly available, allowing stakeholders to assess the supplier’s compliance with ethical sourcing standards. The template should be designed to facilitate data sharing and collaboration, fostering a culture of accountability. Without verifiable data, the entire system is undermined.
Despite its potential, the implementation of the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template faces several challenges. One major hurdle is the lack of standardized data collection methods across different regions and industries. The complexity of the supply chain – involving numerous intermediaries – makes it difficult to trace the origin of minerals back to specific sources. Another challenge is the prevalence of corruption and lack of transparency in some countries. Furthermore, some suppliers may be reluctant to disclose information due to reputational concerns. Finally, the cost of implementing and maintaining a robust reporting system can be significant. However, these challenges are not insurmountable. With appropriate investment and collaboration, these limitations can be addressed. The key is to prioritize data quality and transparency, and to foster a culture of accountability throughout the supply chain.
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in streamlining the process of creating and utilizing the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template. Blockchain technology, for example, can be used to create a secure and transparent record of mineral sourcing, reducing the risk of fraud and improving traceability. Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to analyze large datasets and identify potential risks. Furthermore, mobile technology can be used to collect data from the field, reducing the need for expensive and intrusive audits. Innovation in data collection and reporting is essential for ensuring the long-term success of this initiative. The adoption of these technologies will undoubtedly enhance the effectiveness of the template and contribute to a more sustainable and ethical mining industry.
The creation and implementation of a robust Conflict Minerals Reporting Template represents a critical step towards promoting responsible sourcing and mitigating the risks associated with conflict minerals. It’s a complex undertaking, requiring collaboration among all stakeholders – miners, suppliers, buyers, governments, and consumers. However, the benefits – increased transparency, improved traceability, and enhanced accountability – far outweigh the challenges. By embracing this standardized framework, businesses can contribute to a more sustainable and ethical mining industry, protecting human rights and preserving the environment. The ongoing evolution of technology and best practices will further refine and enhance the effectiveness of the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template, solidifying its role as a cornerstone of responsible supply chain management. Ultimately, this initiative is not just about compliance; it’s about building a future where mining benefits all stakeholders and respects the rights of communities and the environment.