The cornerstone of any thriving enterprise, regardless of its size or industry, is sound financial planning. Without a clear roadmap for your financial resources, businesses often drift, making reactive decisions rather than proactive, strategic ones. This is precisely why an Annual Business Budget Template Excel is not just a useful tool, but an indispensable asset for effective financial management. It provides a structured framework to forecast income, track expenses, allocate funds, and ultimately measure financial performance against set goals, transforming abstract financial data into actionable insights.
The process of constructing an annual budget can seem daunting, especially for those new to financial planning. The complexity of tracking various revenue streams, differentiating between fixed and variable costs, and projecting future financial scenarios can quickly overwhelm an unorganized approach. However, with the right template, much of this complexity is streamlined, allowing business owners and financial managers to focus on analysis and strategic decision-making rather than manual data compilation.
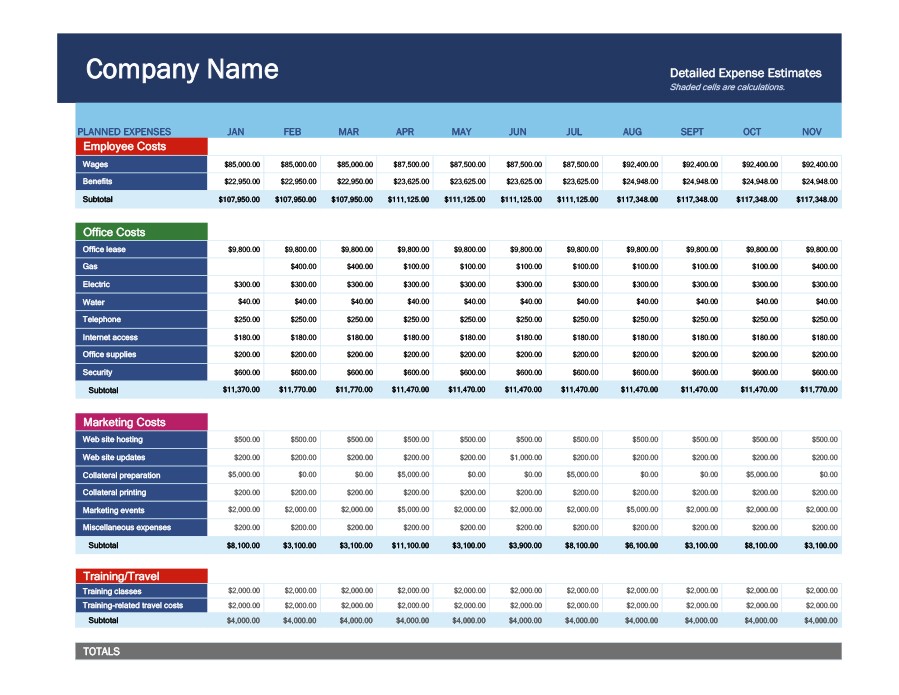
Leveraging Excel for your annual business budget offers unparalleled flexibility and power. Its spreadsheet capabilities allow for dynamic calculations, “what-if” scenario planning, and easy customization to fit the unique nuances of any business model. From intricate formulas that automatically calculate profit margins to visually compelling charts that highlight spending patterns, an Excel template empowers users to gain a granular understanding of their financial health, fostering greater accountability and informed decision-making across all departments.
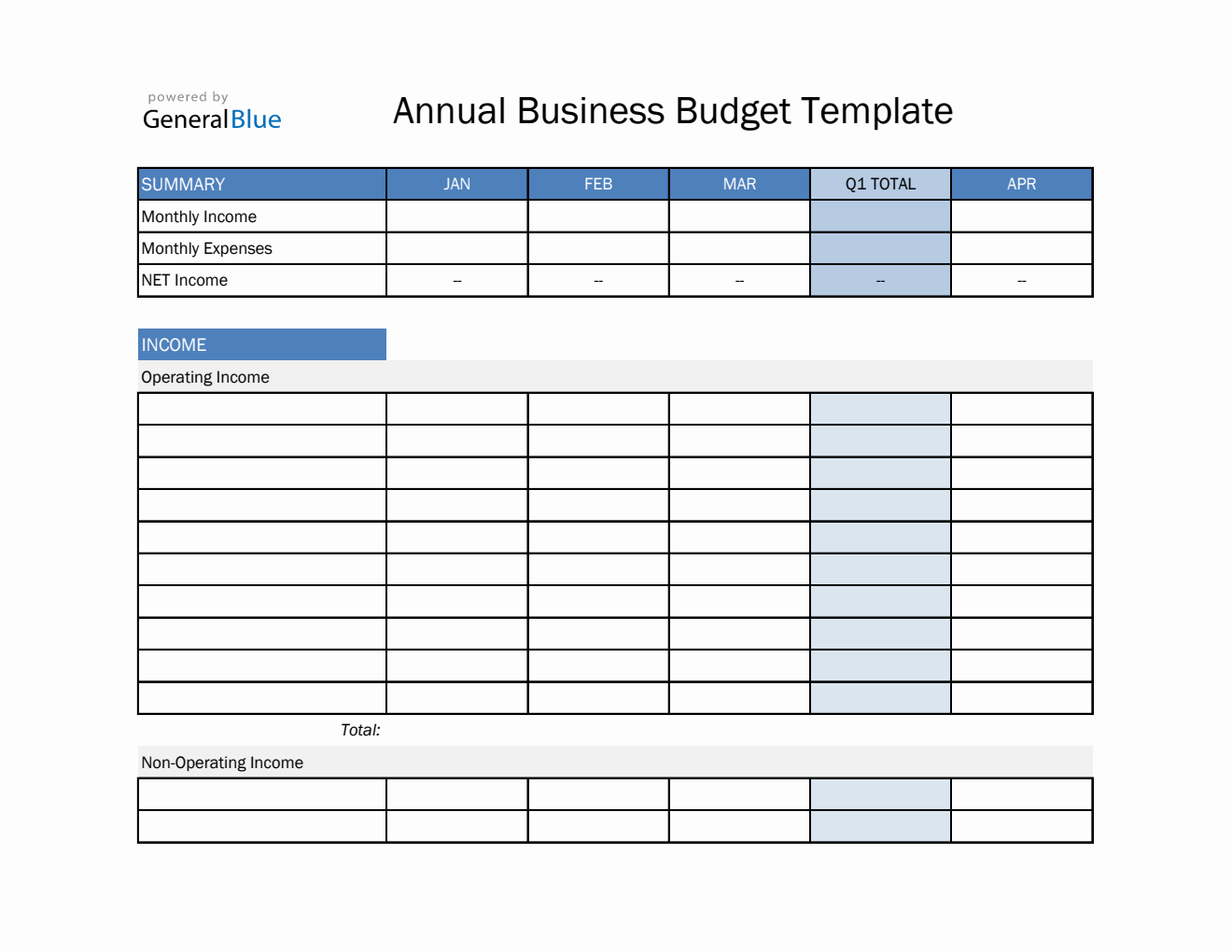
Ultimately, a well-crafted annual budget serves as a compass, guiding your business through the financial year. It helps identify potential shortfalls before they become crises, highlights areas of overspending, and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently towards achieving growth objectives. By embracing the structured approach offered by an Annual Business Budget Template Excel, businesses can move beyond mere survival to planned prosperity, building a resilient financial future.

An annual business budget is far more than just a list of numbers; it’s a strategic financial document that acts as a blueprint for your company’s financial year. Its importance permeates every aspect of business operations, from day-to-day spending to long-term strategic planning. Without a budget, businesses often operate in the dark, leading to inefficiencies, missed opportunities, and potential financial distress.

One of the primary roles of an annual budget is to facilitate strategic resource allocation. It forces businesses to meticulously review their financial capacity and decide where money should be spent to generate the greatest return. This involves prioritizing investments, whether in new equipment, marketing campaigns, or talent acquisition, ensuring that every dollar contributes to the company’s overarching goals. A budget brings clarity to financial decision-making, moving away from impulsive spending towards deliberate, goal-oriented expenditures.
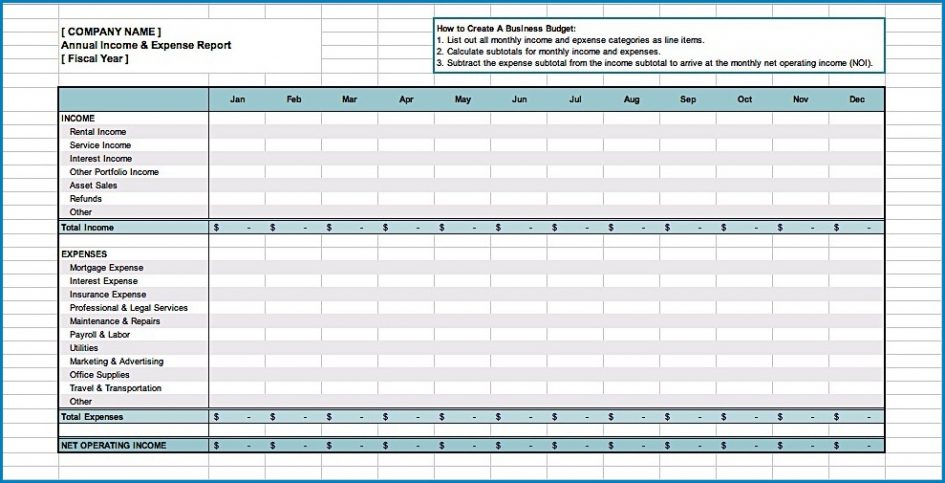
Furthermore, a budget serves as a crucial tool for performance measurement and control. By establishing clear financial targets for revenue, expenses, and profitability, it provides a benchmark against which actual financial performance can be continually compared. This variance analysis allows management to quickly identify deviations, understand their root causes, and implement corrective actions. It promotes financial discipline throughout the organization, holding departments and individuals accountable for their spending and revenue generation efforts.
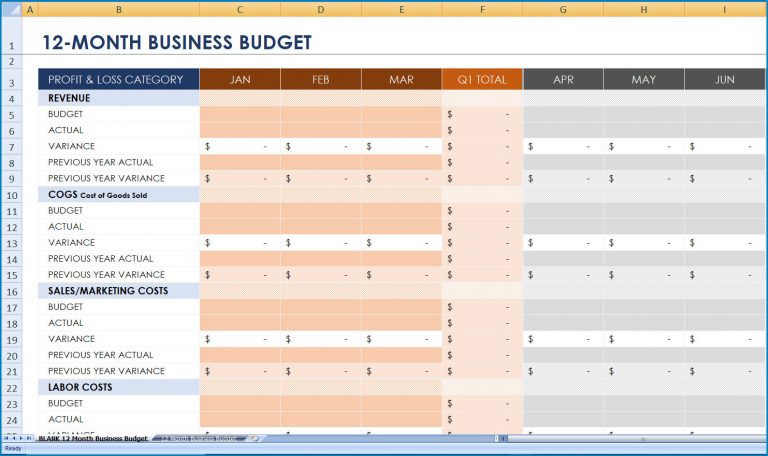
Beyond internal controls, an annual budget is also vital for securing financing and attracting investors. Lenders and investors require a clear understanding of a business’s financial health and future projections. A well-researched and realistic budget demonstrates financial prudence, strategic foresight, and a clear path to profitability, significantly enhancing a company’s credibility and attractiveness to external stakeholders. It proves that the business has a viable plan for managing funds and generating returns.

Finally, the budgeting process itself fosters communication and alignment within the organization. Developing a comprehensive budget typically requires input from various departments, prompting cross-functional discussions about goals, challenges, and resource needs. This collaborative effort ensures that all parts of the business are working towards common financial objectives, creating a unified and cohesive strategy for the year ahead.
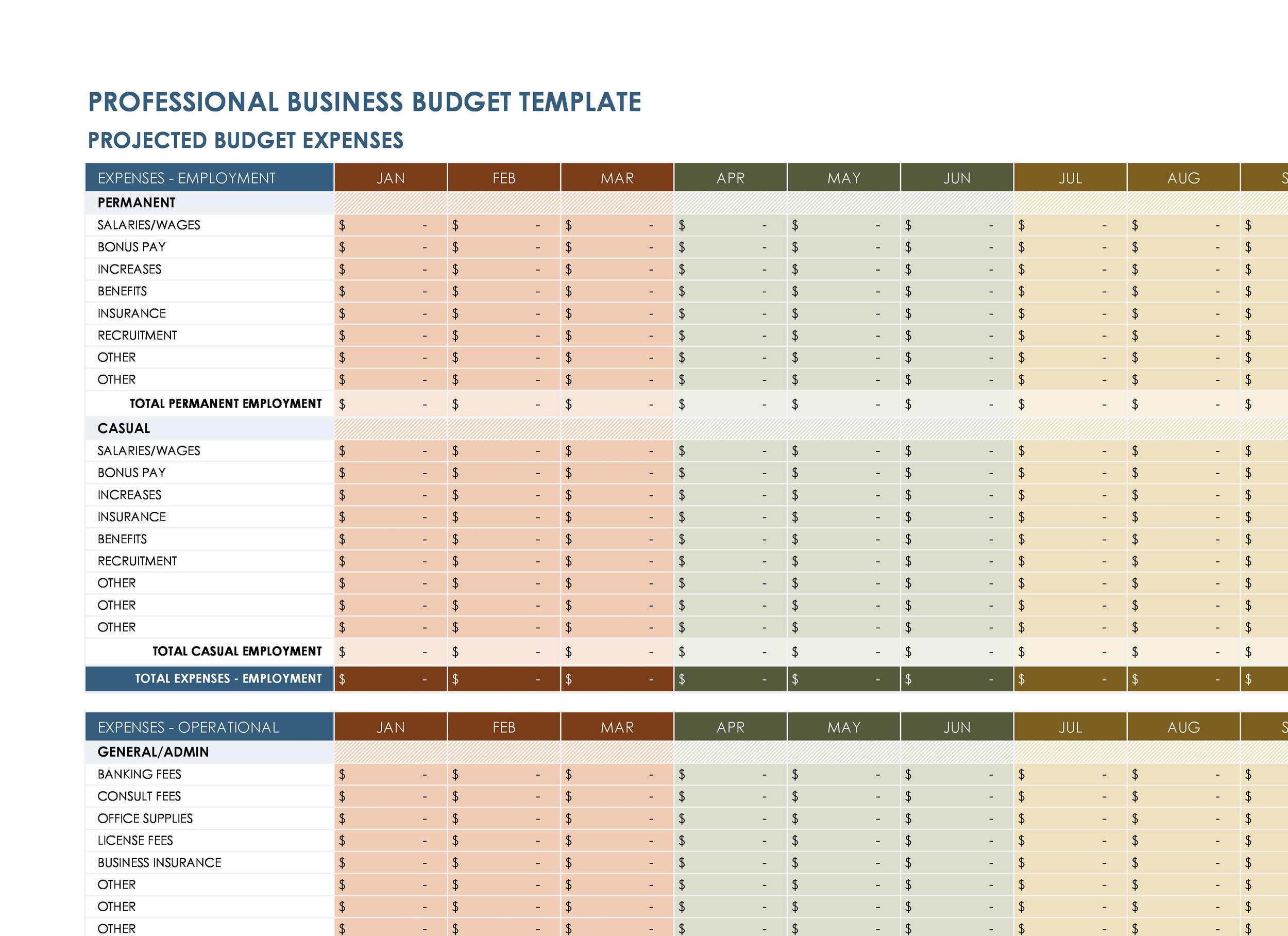
An effective Annual Business Budget Template Excel isn’t just about rows and columns; it’s about intelligent design that simplifies complex financial processes and empowers users. The best templates are intuitive, comprehensive, and flexible enough to adapt to diverse business needs. Understanding the characteristics of a high-quality template can significantly impact the efficiency and accuracy of your budgeting efforts.
A top-tier template typically includes several key sections designed to capture all relevant financial data. It starts with a clear revenue projection area, allowing for detailed forecasts of sales, service income, and other miscellaneous revenues, often broken down by month or quarter. This section should be flexible enough to accommodate different pricing models, sales volumes, and market growth assumptions.
Equally important is the comprehensive tracking of expenses. This usually involves separate categories for fixed costs (rent, insurance, salaries) and variable costs (cost of goods sold, marketing expenses, utilities that fluctuate with activity). A good template will also include sections for one-time capital expenditures and loan repayments, ensuring a holistic view of outgoing cash. The ability to categorize and sub-categorize expenses is crucial for detailed analysis and identifying areas for cost reduction.
Beyond simple input fields, an effective template leverages Excel’s power for automated calculations and summaries. This includes built-in formulas for calculating gross profit, net profit, operating expenses ratios, and various cash flow metrics. It should offer a clear summary dashboard that presents key financial indicators at a glance, allowing users to quickly grasp the overall financial health without sifting through granular data. Visual elements like charts and graphs are invaluable here, providing immediate insights into trends and performance.
Customizability is paramount. No two businesses are exactly alike, so the ability to easily add, remove, or modify categories for revenue and expenses is a must-have. A truly great Annual Business Budget Template Excel will also incorporate scenario planning capabilities. This means allowing users to easily adjust key assumptions (e.g., a 5% increase in sales, a 2% cut in marketing spend) to see their potential impact on the bottom line. This “what-if” analysis is critical for strategic decision-making and risk mitigation.
Year-over-year comparison features are another hallmark of an advanced template. This allows businesses to compare their current year’s budget and actual performance against previous years, providing valuable context and helping to refine future projections. Moreover, the integration of cash flow projections is vital. While a profit and loss statement shows profitability, a cash flow statement reveals the actual liquidity of the business, ensuring it has enough cash to meet its short-term obligations.
Finally, an effective template emphasizes ease of use. It should be well-organized with clear labels, consistent formatting, and perhaps even embedded instructions or data validation rules to minimize errors. While some advanced templates might require a basic understanding of Excel functions, the core functionality should be accessible to users with varying levels of spreadsheet proficiency.
Developing an annual business budget requires a systematic approach to capture all financial inflows and outflows. A comprehensive budget is built upon several critical components, each contributing to a complete financial picture and facilitating informed decision-making.
The starting point for any budget is an accurate projection of revenue. This involves forecasting all sources of income your business expects to generate over the year. For most businesses, this primarily means sales revenue from products or services. Factors to consider include historical sales data, market trends, planned marketing efforts, new product launches, pricing strategies, and economic forecasts. It’s often beneficial to break down revenue by product line, service offering, or even customer segment to gain a more granular view. Don’t forget other potential income streams, such as interest income, rental income, or proceeds from asset sales.
Fixed expenses are costs that do not change significantly with the level of business activity or production volume within a relevant range. These are typically predictable and recurring. Examples include:
* Rent or lease payments for office space, retail locations, or warehouses.
* Salaries and benefits for administrative staff, managers, and other personnel whose compensation isn’t tied directly to sales.
* Insurance premiums (liability, property, health).
* Loan repayments (principal and interest).
* Software subscriptions and licensing fees.
* Depreciation on assets.
Budgeting for fixed expenses is usually straightforward, but it’s important to account for any anticipated changes, such as lease renewals with adjusted rates or planned salary increases.
In contrast to fixed costs, variable expenses fluctuate directly with the level of business activity. The more products you sell or services you provide, the higher these costs will be. Key examples include:
* Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Raw materials, manufacturing costs, and direct labor directly associated with producing goods.
* Sales commissions: Payments to sales staff based on sales performance.
* Marketing and advertising costs directly tied to specific campaigns or sales volumes.
* Shipping and packaging costs.
* Utilities (electricity, water) that vary with usage.
* Hourly wages for production staff or temporary employees based on workload.
Accurately forecasting variable expenses requires a good understanding of your sales forecasts and the per-unit cost of production or service delivery.
Beyond recurring operational costs, businesses often incur one-time expenses or invest in capital expenditures. These are significant investments in assets that will provide long-term benefits to the business. Examples include:
* Purchasing new machinery, equipment, or vehicles.
* Renovating office space or facilities.
* Developing new software or intellectual property.
* Large marketing campaigns or R&D projects that are not recurring.
These expenditures need to be budgeted separately as they can have a substantial impact on cash flow, even if they are amortized or depreciated over time for accounting purposes.
While revenue and expense projections show profitability, cash flow projections are crucial for understanding liquidity. A business can be profitable on paper but still run out of cash if receivables are slow or large expenses are due before income is received. Cash flow projections track the actual movement of cash in and out of the business, considering when payments are received and when bills are paid. This component helps identify potential cash shortages and enables proactive planning for financing or expense deferrals.
Adopting an Annual Business Budget Template Excel can transform your financial planning, but only if used effectively. Here’s a practical, step-by-step guide to help you leverage these powerful tools for your business.
Begin by selecting an Annual Business Budget Template Excel that best fits your business type and complexity. Many free and paid options are available online, ranging from simple spreadsheets to sophisticated models with built-in dashboards. Once selected, customize it. This means:
* Renaming categories: Adjust revenue and expense categories to align precisely with your business’s accounting structure (e.g., “Software Subscriptions” instead of just “Utilities”).
* Adding specific line items: Insert rows for unique income streams or expenses specific to your industry or operations.
* Setting up timeframes: Ensure the template is broken down into monthly or quarterly periods that suit your review cycle.
Before you can project the future, you need to understand the past. Collect your financial statements from the previous one to three years, including:
* Income Statements (P&L): To understand past revenues and expenses.
* Balance Sheets: To see assets, liabilities, and equity.
* Cash Flow Statements: To analyze actual cash inflows and outflows.
* Bank Statements and General Ledgers: For granular detail on transactions.
This historical data provides a realistic baseline for your future projections and helps you identify trends.
Based on your historical data, market research, sales pipeline, and any planned strategic initiatives (e.g., new product launches, pricing changes), project your revenue for each month or quarter of the upcoming year. Be realistic but also ambitious.
* Start with sales volume: Estimate the number of units or services you expect to sell.
* Apply pricing: Multiply volume by your average selling price to get gross revenue.
* Account for discounts/returns: Subtract these to arrive at net revenue.
* Include other income: Don’t forget any non-sales revenue streams.
Next, itemize all your projected expenses.
* Fixed Expenses: Input these directly. Look for known changes like rent increases or new salary hires.
* Variable Expenses: These will be linked to your revenue projections. For example, if COGS is 30% of sales, apply this percentage to your projected revenue.
* Capital Expenditures: List any planned large purchases or investments.
* Debt Service: Include principal and interest payments for any loans.
Be thorough and consider every potential outflow of cash. It’s often better to overestimate expenses slightly than to underestimate them.
Translate your revenue and expense forecasts into a cash flow projection. This involves considering the timing of cash receipts and disbursements.
* Receivables: How long does it typically take customers to pay after invoicing?
* Payables: When are your bills due (e.g., net 30, net 60)?
* Capital Expenditures: When will these large payments actually leave your bank account?
This step is critical for identifying potential cash flow gaps, even if your business is profitable on paper.
Once all data is entered into your Annual Business Budget Template Excel, take time to review it meticulously.
* Variance Analysis: Compare your budget to historical actuals. Are your projections reasonable?
* Scenario Planning: Use Excel’s capabilities to perform “what-if” analysis. What happens if sales are 10% lower? What if a key expense increases by 5%?
* Seek Feedback: Share the draft budget with key stakeholders (department heads, senior management) for their input and buy-in.
* Refine: Make adjustments based on your analysis and feedback. The first draft is rarely the final one.
Remember, a budget is a living document. It should be monitored regularly and adjusted as circumstances change throughout the year.
While a fundamental Annual Business Budget Template Excel provides a solid foundation, embracing advanced features and best practices can significantly enhance its utility and strategic value. Moving beyond simple data entry transforms your budget into a dynamic, proactive financial management tool.
One of Excel’s most powerful capabilities is its ability to perform scenario planning and sensitivity analysis. Instead of creating a single, static budget, develop multiple versions: a “best-case,” “most likely,” and “worst-case” scenario. This involves adjusting key variables (e.g., sales growth rates, cost of goods sold percentages, marketing spend efficiency) across these different scenarios. Advanced templates often have built-in toggles or data tables to facilitate this. This practice helps businesses prepare for various market conditions, assess potential risks, and develop contingency plans. It reveals how sensitive your bottom line is to changes in specific inputs, providing deeper strategic insights.
Simply creating a budget is not enough; continuous monitoring is crucial. Implementing variance analysis involves regularly comparing actual financial results against your budgeted figures. An advanced Annual Business Budget Template Excel should automate this comparison, highlighting significant discrepancies. Beyond just showing the difference, the template can be designed to calculate the percentage variance and even flag variances that exceed a pre-defined threshold. This automation allows for quick identification of areas requiring attention, whether it’s an unexpected revenue shortfall or an expense overrun, enabling timely corrective action. Reporting features that automatically generate monthly or quarterly performance reports from your budget data are also invaluable.
Traditional annual budgets can become outdated quickly in a fast-paced business environment. A rolling forecast overcomes this limitation by continuously updating the budget. For example, after the first quarter, you might drop the past quarter and add a new quarter to the end, always maintaining a 12-month forward-looking view. This practice keeps your financial projections fresh and relevant, reflecting current market conditions and internal performance. An Annual Business Budget Template Excel can be designed with linked sheets and dynamic date ranges to easily accommodate rolling forecasts, ensuring your financial compass is always pointing accurately.
For businesses using accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero, SAP), the ultimate best practice is to explore ways to integrate your Excel budget with these systems. While direct, seamless integration can be complex, even partial automation—like importing actual data from your accounting software into your budget template with minimal manual manipulation—can save significant time and reduce errors. Some advanced Excel users might even leverage Power Query or VBA to pull data automatically, creating a more robust and less labor-intensive process for budget vs. actual comparisons.
A large organization benefits from breaking down the master annual budget into departmental budgets. An effective Annual Business Budget Template Excel can be structured to consolidate individual departmental budgets into the overall company budget. This allows department heads to manage their own specific financial targets, fostering greater accountability. Drill-down capabilities, where you can click on a summary number and see the underlying detailed line items, are essential for managers to understand the composition of their budget figures and make informed decisions.
Selecting the optimal Annual Business Budget Template Excel is a critical decision that can profoundly impact the efficiency and accuracy of your financial planning. With a plethora of options available, ranging from free online downloads to sophisticated commercial tools, understanding what to look for is key.
The first step in choosing a template is to honestly evaluate your business.
* Small Businesses/Startups: A simpler template focusing on core revenue and expense categories might suffice. Overly complex templates can introduce unnecessary overhead. Look for templates that are intuitive and don’t require advanced Excel skills.
* Medium to Large Businesses: As complexity grows, you’ll need templates with more detailed categorization, departmental budgeting capabilities, advanced scenario planning, and robust reporting features. Scalability and the ability to integrate with existing financial data are important considerations.
While many budgeting principles are universal, certain industries have unique financial characteristics.
* Retail/Manufacturing: May require detailed inventory management, COGS analysis, and production cost breakdowns.
* Service-Based Businesses: Will need strong emphasis on labor costs, project-based revenue, and utilization rates.
* Non-Profits: Often require specific sections for grant tracking, donor contributions, and program-specific expenses.
Look for templates that are either specifically designed for your industry or are highly customizable to incorporate these nuances.
Beyond basic input fields, consider the advanced features that will add value:
* Automated Calculations and Formulas: Does the template automatically calculate totals, percentages, and financial ratios, reducing manual entry errors?
* Dashboard and Visualization: Are there clear, digestible summary dashboards with charts and graphs to quickly assess financial health?
* Scenario Planning: Does it allow for “what-if” analysis to model different outcomes?
* Cash Flow Projections: Is there a dedicated section for detailed cash flow forecasting, or is it purely P&L focused?
* Variance Analysis: Does it facilitate easy comparison of actuals vs. budget?
* User-Friendliness: Is the layout logical, with clear instructions and a clean design?
* Support and Documentation: For paid templates, what kind of support or user guides are provided?
Choose a template that can grow with your business. A template that works perfectly today might become restrictive next year if your business expands, adds new revenue streams, or departmentalizes. Look for templates built with a flexible structure that allows for easy addition of new categories, periods, or departmental sheets without breaking existing formulas. The ability to integrate with future accounting software is also a forward-thinking consideration.
By carefully weighing these factors, you can select an Annual Business Budget Template Excel that not only meets your current budgeting needs but also supports your business’s future growth and financial stability.
While an Annual Business Budget Template Excel is an invaluable asset, its effectiveness can be severely undermined by common pitfalls. Being aware of these traps can help businesses maximize the utility of their budgeting efforts and avoid financial missteps.
One of the most frequent mistakes is creating a budget based on overly optimistic (or pessimistic) projections.
* Overly Optimistic Revenue: Assuming exponential sales growth without a solid marketing plan, market research, or historical precedent can lead to overspending and cash flow crises.
* Underestimated Expenses: Forgetting to budget for periodic costs (e.g., annual software renewals, quarterly taxes), underestimating variable costs, or ignoring potential cost increases (e.g., inflation, rising material costs) will quickly derail a budget.
Solution: Always base projections on historical data, realistic market analysis, and a clear understanding of your operational capacity. Use scenario planning to model best-case, worst-case, and most-likely outcomes, allowing for flexibility.
A budget is not a static document; it’s a living financial roadmap that requires continuous monitoring. Creating an Annual Business Budget Template Excel and then only looking at it again at year-end is a recipe for disaster.
Solution: Schedule regular (monthly or quarterly) budget review meetings. Compare actual performance against budgeted figures. Investigate significant variances and understand their causes. Adjust the budget as needed to reflect new information or unforeseen circumstances, treating it as a dynamic tool.
Many businesses focus solely on profit and loss (P&L) statements within their budget, overlooking the critical aspect of cash flow. A business can be profitable on paper but still run out of cash if revenue collection is slow or large expenses are due before money comes in.
Solution: Ensure your Annual Business Budget Template Excel includes detailed cash flow projections. Track the timing of cash receipts and disbursements. Pay close attention to working capital and plan for potential cash shortages, especially during periods of high growth or seasonal fluctuations.
If department heads or key managers are not involved in the budgeting process, they are less likely to “own” their budget and adhere to its limits. This can lead to resistance, overspending, or a general disregard for financial discipline.
Solution: Involve relevant stakeholders in the budget creation process. Seek their input on revenue projections and expense needs for their respective areas. Explain the strategic rationale behind budget allocations. When people feel a sense of ownership, adherence improves dramatically.
While advanced features are beneficial, an overly complex Annual Business Budget Template Excel can be intimidating and counterproductive, especially for smaller businesses or those new to budgeting. Too many tabs, intricate formulas, or unnecessary detail can lead to confusion and errors.
Solution: Start with a template that matches your current business complexity. As your business grows and your financial sophistication increases, you can gradually incorporate more advanced features or switch to a more robust template. Prioritize clarity and ease of use over excessive detail.
Unexpected events (e.g., economic downturns, natural disasters, sudden market shifts, equipment breakdown) can significantly impact a business’s finances. A budget with no buffer or contingency plan is highly vulnerable.
Solution: Always include a contingency fund or an “unallocated” budget line item (typically 5-10% of total expenses) to cover unforeseen costs. This allows for flexibility without derailing the entire financial plan.
By actively avoiding these common pitfalls, businesses can transform their Annual Business Budget Template Excel from a static document into a powerful, dynamic tool that truly guides financial success and fosters sustainable growth.
In the competitive landscape of modern business, strategic financial management is not merely an advantage; it is a fundamental requirement for survival and growth. At the heart of this management lies the annual business budget. As we have explored, an Annual Business Budget Template Excel serves as an indispensable tool, providing a structured, flexible, and comprehensive framework for forecasting, tracking, and analyzing your company’s financial journey throughout the year.
From setting realistic revenue targets and meticulously detailing both fixed and variable expenses to projecting critical cash flows and planning for capital investments, a well-utilized Excel template empowers businesses with unparalleled clarity. It moves financial planning beyond guesswork, offering a data-driven approach that fosters accountability, identifies potential challenges before they escalate, and highlights opportunities for greater efficiency and profitability. The ability to customize, conduct scenario analysis, and automate comparisons against actual performance transforms a simple spreadsheet into a powerful strategic asset.
While the process of creating and maintaining an annual budget demands discipline and attention, the rewards are substantial. It facilitates informed decision-making, strengthens financial control, attracts investor confidence, and ultimately aligns the entire organization towards common financial objectives. By consciously avoiding common pitfalls such as unrealistic projections or a lack of continuous review, businesses can fully harness the power of their budget. Embracing an Annual Business Budget Template Excel is not just about crunching numbers; it’s about building a robust financial foundation that supports sustained success and propels your business confidently into the future.