The world of project management and problem-solving often relies on visual tools to understand complex issues and facilitate effective solutions. One such tool is the Fishbone Diagram, also known as a Ishikawa diagram or cause-and-effect diagram. These diagrams offer a structured approach to identifying the root causes of problems, leading to more targeted and efficient interventions. Blank Fishbone Diagram Template Word is a readily available resource, empowering individuals and teams to create these visual representations of potential issues. This article will delve into the principles of Fishbone Diagrams, explore their benefits, and provide a practical guide to creating and utilizing them effectively. Understanding how to construct and interpret a Fishbone Diagram is a valuable skill for anyone involved in planning, problem-solving, or process improvement. It’s more than just a pretty diagram; it’s a powerful tool for uncovering hidden causes and driving meaningful change.
The Fishbone Diagram originated in the 1950s as a way to systematically analyze problems. It was developed by W. L. Edwards and his team at Bell Labs, initially intended to help engineers diagnose the causes of equipment failures. The core concept is to break down a problem into its component parts, allowing for a more thorough examination of each element. Instead of simply listing symptoms, the diagram forces you to consider why something is happening, leading to a deeper understanding of the underlying issues. The visual nature of the diagram makes it easy to identify patterns and relationships, facilitating collaborative problem-solving. It’s a remarkably versatile tool applicable across diverse fields, from manufacturing and healthcare to software development and customer service. The initial focus was on identifying the “5 M’s” – Man, Machine, Method, Material, and Measurement – but modern variations often incorporate additional categories like People, Process, and Environment.
The benefits of utilizing a Fishbone Diagram are numerous and significant. Firstly, it dramatically improves problem identification. By systematically exploring potential causes, teams can uncover root issues that might otherwise be missed. Secondly, it promotes collaboration. The diagram’s visual format encourages team members to contribute their insights and perspectives, fostering a shared understanding of the problem. Thirdly, it facilitates prioritization. By visually representing the potential causes, it’s easier to identify the most critical issues requiring immediate attention. Finally, it provides a framework for developing effective solutions. The identified root causes can then be addressed through targeted interventions, leading to improved outcomes. A well-constructed Fishbone Diagram isn’t just a diagram; it’s a roadmap to improvement. It’s a tool for continuous learning and refinement.
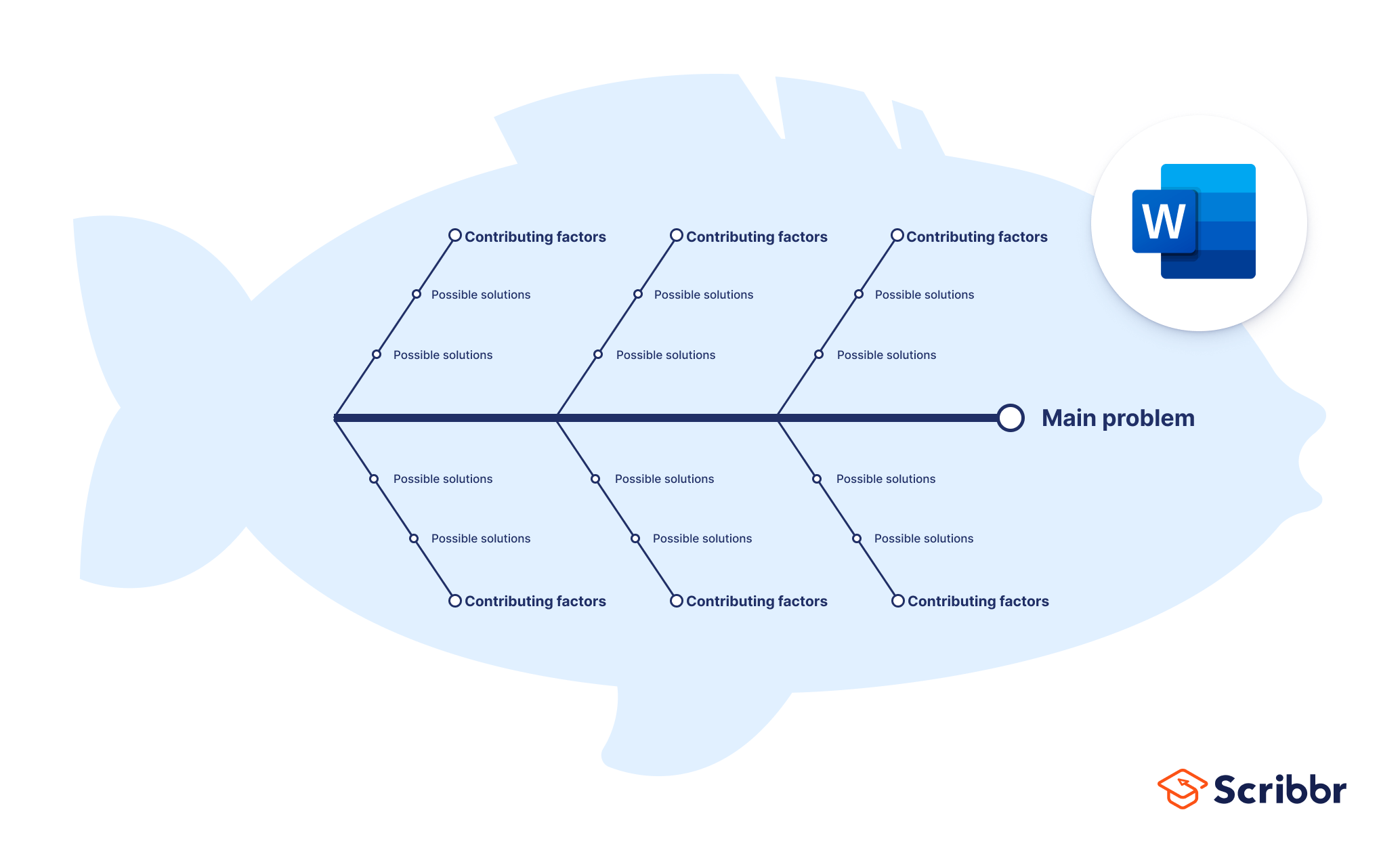
Let’s explore the key components of a Fishbone Diagram. The core elements are typically represented as six main categories, often visualized as six circles arranged in a spiral. These categories are:
Within each of these categories, further sub-categories are often included to provide more granular detail. For example, under “Man,” you might have sub-categories like “Training,” “Skills,” and “Communication.” The specific categories and their arrangement will vary depending on the nature of the problem being addressed. It’s crucial to remember that the Fishbone Diagram isn’t a rigid structure; it’s a flexible tool that can be adapted to suit the specific needs of the situation.

Now, let’s look at some specific examples of how to use a Fishbone Diagram to tackle different types of problems.
Let’s consider a scenario where customer service is experiencing a high volume of complaints. A Fishbone Diagram could be used to systematically analyze the root causes of these issues.
By systematically exploring these categories, the team can identify the underlying factors contributing to the high volume of complaints. For example, they might discover that inadequate training is a major contributor, leading to inconsistent service quality.
In a manufacturing environment, a Fishbone Diagram can be used to identify bottlenecks in the production process.
By examining these factors, the team can pinpoint the specific steps that are causing delays and inefficiencies. For instance, they might discover that a particular machine is consistently overloaded, leading to bottlenecks.
In software development, a Fishbone Diagram can be used to analyze the causes of project delays.
By systematically exploring these categories, the team can identify the root causes of delays, such as poor communication or inadequate resources.
Analyzing website traffic can reveal a multitude of potential problems. A Fishbone Diagram can be used to systematically investigate these issues.
By examining these factors, the team can identify the root causes of website traffic issues, such as poor SEO performance or outdated content.
The Blank Fishbone Diagram Template Word is a powerful and versatile tool for problem-solving and process improvement. Its visual nature and structured approach make it easy to identify root causes, facilitate collaboration, and prioritize interventions. By consistently applying the principles of the Fishbone Diagram, individuals and teams can significantly improve their ability to understand and address complex challenges, ultimately leading to better outcomes. The key to effective utilization lies in a thorough understanding of the diagram’s components and a commitment to systematically exploring each category. Remember that the Fishbone Diagram is a dynamic tool, and its effectiveness depends on ongoing analysis and refinement. Continuous monitoring of key metrics and a willingness to adapt the diagram to reflect changing circumstances are essential for maintaining its value. Ultimately, the blank template provides a starting point for a deeper dive into the problem, empowering teams to take targeted action and drive meaningful change.